Harley FX Models (1971 through 1983)
Article by Mark Trotta
The 1971 Super Glide was the first of the Harley FX models. Although not a big seller at the time, it is considered to be the first factory custom motorcycle.

Designed by Willie G Davidson, grandson of company co-founder William Davidson, the Super Glide combined the lighter, thinner front-end of a Sportster with a Big-Twin frame and Shovelhead motor. At 560 pounds, it was 150 pounds lighter than an FL Touring model, and 60 pounds heavier than a Sportster.
While FL models continued use of a 7" headlamp, FX models shared the Sportster XLCH's smaller 5-3/4" headlamp. Fat-Bob gas tanks and dash unit were from the FL.
Transmission
Both FL and FX models left the factory with the same shift pattern - one down, three up. The difference was, the shifter drum for FL models was designed for the shift linkage to be connected to the lower side of the drum.
The FX drum was reversed, so the linkage was also reversed (connects to top of drum).
Read: Harley 4-Speed Transmission Differences
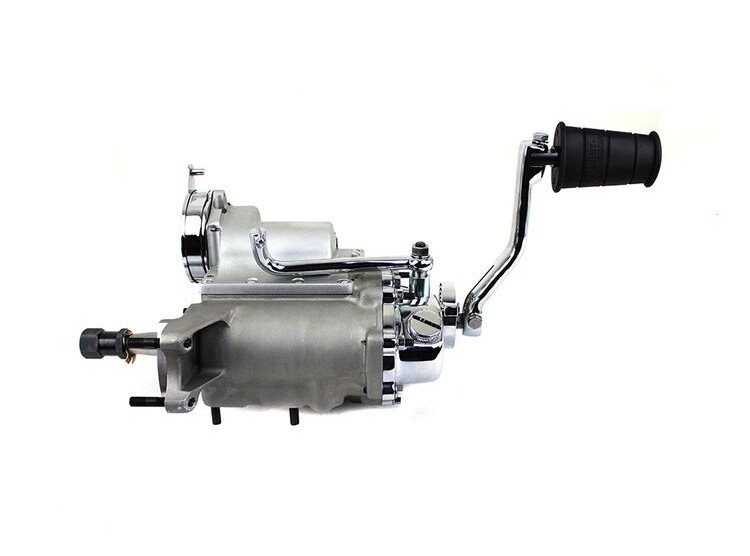

Read: Harley 4-Speed Mainshaft and Countershaft Differences
1971/1972 FX
The first-year Super-Glide featured a one-year-only fiberglass "boat-tail" seat/fender combination. Restyled with a more traditional seat and rear fender, the 1972 version looked much cleaner.
1974 Super Glide
In it's third year of production, a smaller, one-piece three-gallon gas tank replaced the larger FL Fat-Bob tanks. The Super-Glide FX was soon joined by the FXE, an electric-start version.

Both FX and FXE models had the one-piece gas tank, which made the bike narrower and a little easier to ride aggressively.
The FXE began outselling the FX, then out-selling the FLH touring bike, becoming the most popular Harley Big-Twin model.
Harley FX Carburetor
Early models were fitted with a Bendix carburetor (1971 through 1975). In 1974, Harley FL Touring models switched from Bendix carburetors to Keihin, while the FX models continued using the Bendix carb.

Read: Best Carb For Shovelhead
======================
Early Super Glide Forks
Super Glide fork tubes where shared with early Sportsters, which go back to the 1956 Harley K-model. The 33.4mm diameter tubes looked kind of spindly attached to a Big-Twin frame.
In 1973, fork tube diameters were increased to 35mm, manufactured first by Kayaba (1973-1975) and then Showa (both Japanese companies).
Also in 1973, front disc brakes became standard. Early models have the "pie-slice" front brake caliper, later models have dual-disc calipers.
======================
Harley-Davidson Low Rider
In 1977, the FXS Low Rider was introduced, featuring a low 26-inch seat height, shorter rear shocks, alloy wheels front and rear, twin front disc brakes, and extended forks with a 32-degree rake. The Fat-Bob tanks returned, featuring a dashboard with speedometer and tachometer.

Unlike the Super Glide, the Low Rider was an instant hit, outselling other Harley Big Twins in it's first full year of production. All three FX models now sported Fat-Bob tanks, with their own center divider.
======================
74ci vs 80ci Shovelhead
From 1966 to 1977, the Shovelhead motor displaced 1200cc. The cylinders had a 3.44" bore with a rod-stroke of 3.97", making 74 cubic-inches.
During production of the 1978 model year, engine size was increased to 1340cc (80 cubic-inches) and was available optionally on Harley FL models. Whereas the 74ci motor was designed to run on premium leaded fuel, the 80ci motor was designed to run on premium unleaded.

The larger engine was offered on FX models starting in 1979.

Externally, the 80 cubic-inch engines had a larger, different air cleaner. Another visual difference is 80ci motors had one less fin on each cylinder.
Cylinder Heads
A cylinder head change was seen in mid-1978. Earlier heads had a lip-style O-ring to seal the intake manifold to the cylinder head. Starting in mid-1978, the O-ring was replaced with a flat band with no lip.
======================
1979 Harley FX Models
The kickstart-only FX was discontinued in 1979. In that same year, the FXEF Fat Bob was introduced, offered with either cast or spoked wheels, and with either the 74 or 80ci motor.
======================
Wide Glide
Based on the Low Rider, the Harley FXWG Wide Glide debuted in 1980. Wide Glide models featured wide chrome front forks with a 21" front tire, dual-disc front brakes, bobbed rear fender, and a flame pattern painted on the gas tank. In addition to the FXWG models, Wide Glide front ends also came on 1980-1983 FWDG Dyna series.

Read: Wide Glide Front-End Conversion
The original FXWG was produced from 1980 through 1986, then re-appearing in 1991 as the FXDWG.
======================
1980-1982 Harley FXB Sturgis
Painted black with red trim, the short-lived Sturgis FXB featured a king/queen seat, belt-drive, and thick-spoked wheels. The fuel tank featured a speedometer, tachometer, and matching filler caps. A two-inch fork extension gave it a mild "chopper" look.
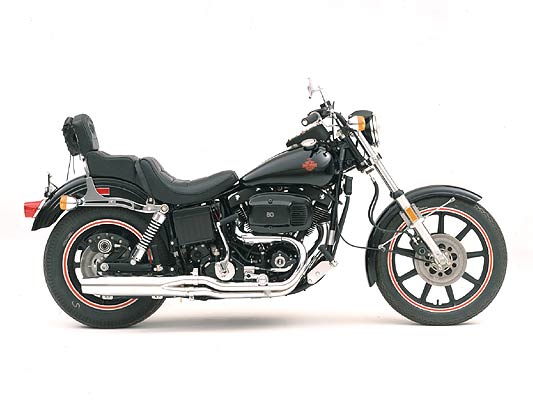

The Harley Sturgis was named after the annual motorcycle rally held in Sturgis, South Dakota. Originally produced only two years, the FXB would re-appear in 1991 on the Dyna platform as the FXDB.
======================
Harley FXR (1982-1994)
Introduced in 1982, the Super Glide II (FXR) differed from the existing FX models in many ways. Where other FX models had solid engine mounting and a four-speed transmission, the FXR shared the rubber-mounted engine and new five-speed transmission with FLT Tour Glide. The new frame was stiffer and offered more ground clearance, making the FXR a better handling bike.
FXR Models
The first-year saw two different models; the FXR Super Glide II with spoke wheels, and the FXRS with cast wheels and two-tone paint.
Only two model year FXR's (1982-1983) were equipped with the Shovelhead engine, subsequent models (1984-1994) were powered by the Evolution motor. The FXR handled well and was fast. It also had less mechanical problems than previous FX models, which helped the bad reputation all Harley-Davidsons suffered during the seventies.
Harley FX vs FXR
The easiest way to tell an FXR from other FX models is by the triangle-shaped side cover.
======================
Chain-Drive to Belt-Drive
In 1983, the Low Rider was converted from chain-drive to belt-drive and given the designation FXSB. Introduced this year was the FXDG Disc Glide, featuring a disc-type rear wheel instead of the wire-spoked wheel of the Super Glide or the solid-spoked wheel of the Low Rider. The FXB model was discontinued.
Harley FX Models
- FXSB Low Rider
- FXE Super Glide
- FXR Super Glide
- FXRS Super Glide
- FXRT Tour Glide
- FXWG Wide Glide
- FXDG Disc Glide

======================
How-To Articles

Read: Rebuild Harley Pie-Slice Caliper

Read: Rebuild Harley Dual Calipers
Read: Rebuild Harley Master Cylinder
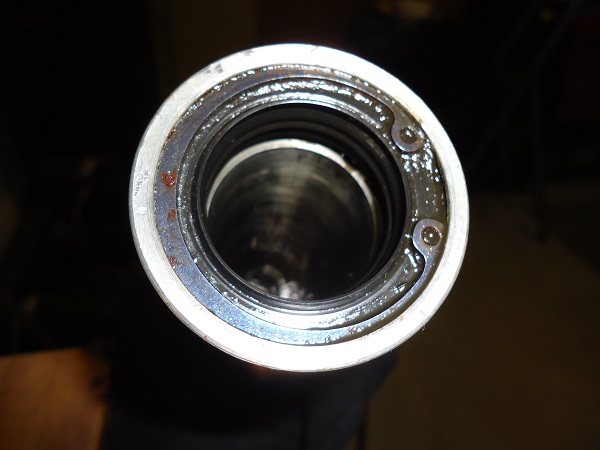

Read: Replace Harley Fork Seals 35mm
======================
Harley FX VIN Numbers
The first two numbers of the VIN are the year and the letters (up to four) are the model code, example, FX or FL. The last numbers are the production number.

Miss Harley-Davidson 1971
Harley FX models should have matching frame and engine numbers if the bike is all original.
From 1970 to 1980, matching VIN numbers appear on both frame and engine.
1979 Harley VIN
In an attempt to curtail theft, the Motor Company used different frame and engine numbers on some 1979 models. The frame numbers didn't match the number stamped on the engines. The first two digits remained the model code.

From 1981 to 1983, a 17-digit VIN appears on the frame, and the engine had a partial VIN.
======================
Related Articles:
Best Carb For Shovelhead
Harley Forks Identification
Convert Harley To Points Ignition
Remove Harley Sprocket Shaft Bearing
Harley Crankcase Lapping Tool and Usage
DIY Harley Engine Stand
